Action Overview: Implementation
Develop a Shared Understanding of Implementation
The Standards Portal is designed with the understanding that changing student outcomes requires implementation of effective instructional practices. The implementation of effective instruction requires structures that are intentionally designed to support teams of educators as they work together to change their instructional practices. In other words, changing student outcomes requires changes in instructional practices and changing instructional practices requires the development of implementation capacity to support those practices.
The implementation research used to design the Portal is the Active Implementation Frameworks developed by the National Implementation Research Network (NIRN). After synthesizing implementation research, NIRN developed five overarching frameworks (referred to as the Active Implementation Frameworks) to help organizations build capacity to sustain changes in their practices. This action is designed to help leadership teams and educators at large become familiar with each of the five Active Implementation Frameworks: Stages, Usable Innovations, Drivers, Teams, and Improvement Cycles. A brief overview of the Active Implementation Frameworks as a whole is provided, followed by a brief overview of each framework.
Why is understanding and using Active Implementation Frameworks important?
Effective implementation capacity is essential to improving education. Shared understanding of the Active Implementation Frameworks and how they interact to impact student outcomes provides stakeholders with a firm foundation from which to build a Standards-based Education (SBE) system--essentially, they provide a structure for addressing the complexities that are needed to ensure that all students are successful.
NIRN’s synthesis of the research resulted in the Formula for Success that is shown below. It elaborates on the understanding referenced in the first paragraph by providing a picture of the overall approach to implementation. This formula shows that in order to attain the desired student outcomes, education systems need Evidence-based Instructional Practices, Effective Implementation, and Enabling Contexts.
NIRN’s Formula for Success
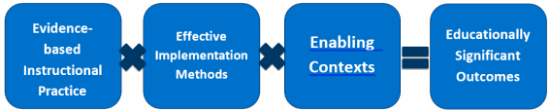
The next diagram has the Active Implementation Frameworks that were listed previously added to the formula followed by a brief description of each framework.
NIRN’s Formula for Success




Icons for each of the Active Implementation Frameworks are shown below. These Frameworks categorize the critical components of effective implementation and provide a structure for approaching implementation. A brief description of each framework is provided below.
Usable Innovations
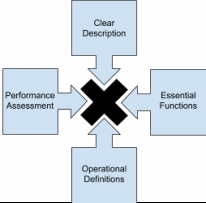
The diagram below shows the criteria for a practice to be a Usable Innovation. Again, since the Usable Innovation in the Portal is an Evidence-based Instructional Practice (EBP), these criteria make it possible for organizations and teams of educators to have shared understanding of the instructional practices that are being implemented. They necessarily lead to the creation of tools to support teacher teams, to collect fidelity data, and to determine what the system needs to do to provide better support for effective use of the EBP.
Criteria for a Usable Innovation
Please note that due to differing references for Usable Innovation used in various professions, the resources accessed in NIRN could also refer to Usable Innovation with different terms such as Usable Intervention and Effective Instruction. The Portal consistently refers to the Usable Innovations as Evidence-based Instructional Practices (EBP)
Teams
Implementation Teams consist of the people who do the work of implementation (Stages, Drivers, and Improvement Cycles) in service to supporting use of the Evidence-based Instructional Practice. They develop and sustain capacities in the system to assure the intended outcomes are realized. Therefore, in the Portal, Leadership Teams are Implementation Teams. Though the Portal focuses on Building or District Leadership Teams, the diagram below shows an aligned set of linked teams supporting implementation of an EBP across several levels in the system. The arrows indicate that information flows in both directions in service to removing barriers to successful use of EBPs.
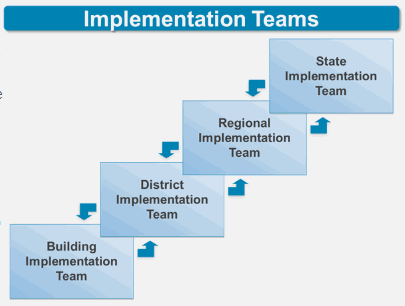
Drivers
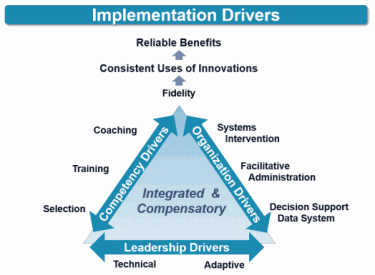
Implementation Drivers are designed to improve the skill levels of teachers, principals, and staff so that students benefit from the EBPs. In other words, Implementation Drivers support the successful use of EBPs. The diagram below provides a more detailed look at the drivers. Each side of the triangle shows a collection of different types of support--all in service to fidelity so that student outcome goals are achieved.
The overarching message is that the system is collecting data to understand impacts of the supports and to provide information that can be used for action planning to improve the supports. In other words, improvement cycles are used to build capacity throughout the system, including the data system, the professional learning system, and the ways in which leadership responds to challenges.
Stages
The stages of implementation help with action planning as they provide guidance to help with efficiency and effectiveness--essentially, with doing the “right work” at the “right time.” As shown in the diagram below, there are four stages. The arrows indicate that this is not a linear process as information learned or changes occurring at one stage, may require work in another stage.
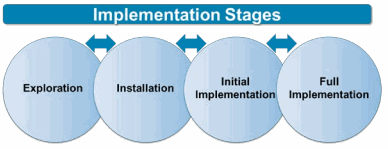
The main emphasis for each stage is provided below.
· Exploration--creating readiness to implement EBPs
· Installation--preparing resources, professional learning, and tools to support EBPs
· Initial Implementation--supporting teachers as they begin to use the EBPs and making adjustments to the supports provided
· Full Implementation--continued work to maintain fidelity to EBPs
Improvement Cycles
Improvement Cycles are the purposeful process of change. Implementation teams use improvement cycles to change on purpose. The diagram below provides more information about improvement cycles.

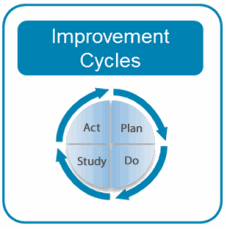
Suggested Activities
How do educators use Portal resources to examine Active Implementation Frameworks?
1. Consider downloading one-pagers with brief descriptions for each Framework and determining how they might be used to help with building shared understanding. Links to each document are provided below.
2. The National Implementation Research Network (NIRN) provides another site, called the Active Implementation Hub (AI Hub). This site is designed to help individuals, teams and organizations learn about and apply the Active Implementation Frameworks. The site provides modules, lessons, planning tools and other resources available to support you in this process. Modules include content, activities, handouts, resources and assessments designed to promote the knowledge and practice of implementation science and scaling-up. Lessons provide additional information on specific implementation tools and practices. In addition, a Learning Plan is provided as a guide for accessing more information about implementation as well as how to apply this understanding. This Learning Plan includes a recommended progression to using the modules, and identifies specific activities, tools, lessons and resources that can be used to provide guidance in the application and installation of the Active Implementation Frameworks and the development of an implementation plan.